Heart valve replacement surgery in Türkiye
Heart valve replacement a normal heart valve that isn’t working properly with an artificial one. An artificial valve is an artificial valve or an alternative to a natural valve.
What is the valve replacement process?
It is designed to mimic the normal opening and closing motions of a normal valve. A prosthetic valve can replace any of the heart valves — mitral, aortic, pulmonary, or tricuspid.
Artificial heart valves fall into two basic categories: artificial mechanical valves and biological valves, which are usually made of animal tissue.
Mechanical valves
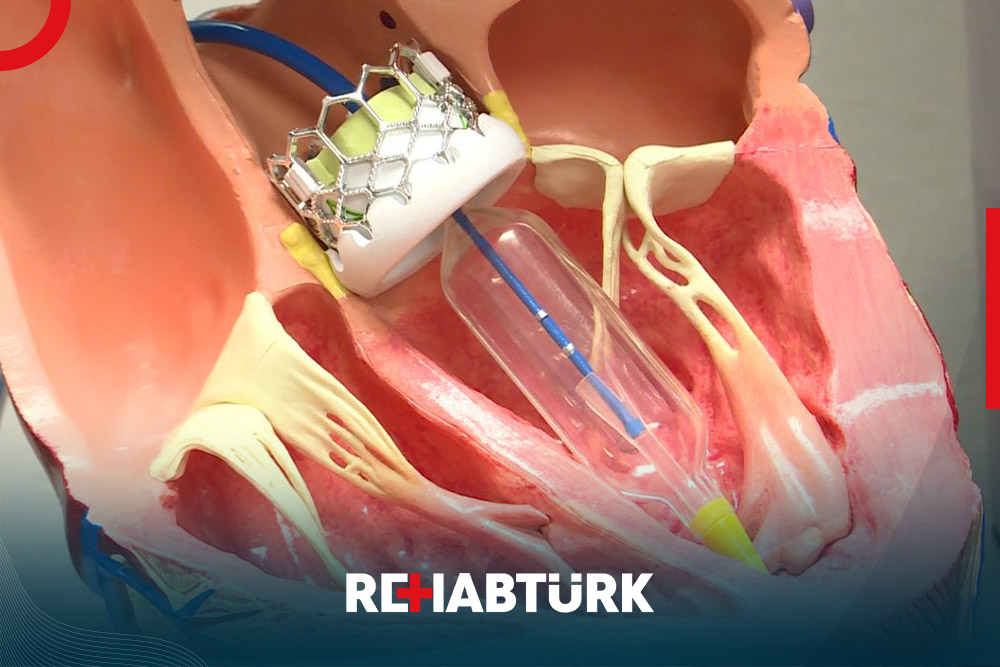
Several different forms of mechanical valves have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in hospitals. Different types differ in the mechanisms they use to open and close the valves.
In general, mechanical valves tend to last longer than biological valves, but they also carry a greater long-term risk of thromboembolism, a floating blood clot that can travel through the circulatory system, causing stroke and other problems .
To help prevent blood clots, people who receive mechanical heart valves must take anticoagulant medications (anticoagulants) for the rest of their lives.
Although mechanical valves are generally used in younger patients because of their durability, the need for anticoagulant medication can complicate pregnancy in young women.
The choice of a mechanical or biological valve is up to the attending physician
What are the reasons for valve replacement?
The reasons for valve replacement are slightly different, depending on which of the four heart valves is involved. As a general guide, however, you may need to replace the valve for any of the following reasons:
- You have a valve that is severely narrowed (stenosis) or leaking (regurgitation) causing severe heart symptoms, such as angina (chest pain), shortness of breath or syncope (fainting spells).
- Although the heart symptoms are not yet severe, diagnostic tests show that you have valve stenosis or regurgitation that is beginning to seriously affect heart function.
- Your heart valve has been severely damaged by endocarditis (inflammation of the heart valve), or you have antibiotic-resistant endocarditis.
- You already have an artificial heart valve, but it needs to be replaced because it’s leaking or malfunctioning, you’ve had frequent blood clots or heart valve infections, or you have bleeding problems related to anticoagulants.
Types of heart valve surgery
Aortic valve replacement
The aortic valve is located on the left side of the heart and acts as an outflow valve. Its job is to allow blood to leave the left ventricle, which is the heart’s main pumping chamber. Its job is also to close so that blood does not leak back into the left ventricle. You may need aortic valve surgery if you have a birth defect or a disease that causes stenosis or regurgitation.
The most common type of congenital anomaly is the bicuspid valve. Normally, the aortic valve contains three sections of tissue, known as leaflets. This is called the tricuspid valve. The defective valve has only two leaves, so it is called the bicuspid valve.
A recent study found that aortic valve replacement surgery has a 94 percent five-year survival rate. These rates depend on:
- Your age
- your general health
- other medical conditions you have
- your heart function
Mitral valve replacement
The mitral valve is located on the left side of the heart. It acts as a flush valve. Its job is to allow blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle. Surgery may be required if the valve is not fully opened or closed completely. When the valve is too narrow, it can make it difficult for blood to enter. This can cause them to reflux, causing pressure in the lungs. When the valve doesn’t close properly, blood can leak back into the lungs. This could be due to a birth defect, infection, or degenerative disease.
The defective valve will be replaced with a metallic prosthetic valve or a biological valve. The metal valve will last a lifetime but requires you to take blood thinners. A biological valve lasts 15 to 20 years, and you won’t be required to take blood-thinning medication.
The success rate of this operation globally is 91%. The following also plays a role in the success rates of the operation:
- Your age
- your general health
- other medical conditions you have
- your heart function
Ask your doctor to help assess your personal risks.
Double valve replacement
Bivalve replacement is the replacement of both the mitral valve and the aortic valve, or the entire left side of the heart. This type of surgery is not as common as other types and the success rate is lower.
Pulmonary valve replacement
The pulmonary valve separates the pulmonary artery, which carries blood to the lungs for oxygenation, and the right ventricle, which is one of the chambers of the heart. Its job is to allow blood to flow from the heart to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. The need for pulmonary valve replacement is usually due to the stenosis restricting blood flow. The stenosis may be caused by a birth defect, infection, or a precancerous syndrome.
Perform the valve installation process
Heart valve replacement surgery is performed under general anesthesia with conventional or minimally invasive techniques. Conventional surgery requires a large incision from your neck down to your navel. If you have less invasive surgery, the incision length may be shorter and you may also reduce the risk of infection.
In order for a surgeon to successfully remove the diseased valve and replace it with a new one, your heart must be immobilized. You will be put on a bypass machine, which keeps your blood circulating and your lungs working during surgery. The surgeon will make incisions in the aorta, through which the valves will be removed and replaced.
recovering from the operation
The majority of artificial valve recipients stay in the hospital for approximately five to seven days. If the surgery was minimally invasive, you may be able to go home earlier. The medical staff will provide pain medication as needed and will monitor your blood pressure , breathing and heart function continuously for the first few days after a heart valve replacement.
Full recovery may take a few weeks or even several months, depending on the rate of recovery and the type of surgery that was performed. Infection is the primary risk immediately after surgery, so keeping your incisions sterilized is of the utmost importance. Always call your doctor right away if you have symptoms that suggest infection, such as:
- Fever
- goosebumps
- Swelling at the incision site
- Increased drainage from the incision site
Follow-up appointments are important and will help your doctor determine when you’re ready to resume your daily activities. Make sure you have a support system in place for the time after surgery. Ask family members and friends to help you around the house and direct you to medical appointments while you recover.
Heart valve replacement surgery in Türkiye
Many patients come to Türkiye for heart valve replacement surgery.
REHABTÜRK HEALTHCARE PROVIDER NETWORK treatment services to patients in addition to transportation, accommodation and full trip coordination services.
Heart valve replacement surgery in Türkiye requires at least 15 nights for patients from abroad.
Patients receive intensive care after the operation to check their condition and satisfaction after the operation in Türkiye. In addition, our patient support team is available 24/7.
