Treatment of glaucoma in the eye (glaucoma) in Türkiye
Treatment of glaucoma in the eye is done in multiple ways and methods, depending on the case. You may need glaucoma surgery (by laser or surgery), or simply medications can treat glaucoma.
What is glaucoma or “blue water”?
Glaucoma is an eye disease that can damage the optic nerve. The optic nerve is responsible for providing the brain with visual information coming from the eyes.
Glaucoma is usually caused by abnormally high pressure inside the eye. And the increased pressure can wear down the optic nerve tissue over time which can lead to vision loss or even blindness!
If caught early, you may be able to prevent further vision loss.
What are the symptoms of glaucoma?
The most common type of glaucoma is called open angle glaucoma . It has no signs or symptoms except for progressive vision loss. For this reason, it is important to have comprehensive eye exams annually so that your ophthalmologist or ophthalmologist can monitor any changes in vision.
Angle-closure glaucoma, also known as narrow -angle glaucoma , is considered a medical emergency, so you should see a doctor immediately if you experience the following:
- severe eye pain
- Nausea.
- vomiting
- redness in the eyes
- Sudden vision disturbances
- See colored rings around the lights.
- Sudden blurred vision .
What causes glaucoma?
The back of the eye continually produces a fluid called water, or the “aqueous humor.” This fluid fills the front of the eye as it is produced. It is then drained through channels in the cornea and iris.
If the channels are partially or completely blocked, the normal pressure in the eye may increase. With increased pressure, the optic nerve may be damaged. You may begin to lose vision as damage to the optic nerve continues.
The cause of increased pressure in the eye is not always known. However, doctors believe that one or more of these factors may play a role:
- Eye expansion drops.
- Blockage of the ducts or poor drainage of fluid in the eye
- Certain medications, such as corticosteroids
- Poor or decreased blood flow to the optic nerve
- high blood pressure
What are the types of glaucoma?
There are five main types of glaucoma :
Open-angle (chronic) glaucoma
“Chronic” open-angle glaucoma has no signs or symptoms other than gradual vision loss. Vision loss may be very slow and irreversible damage may occur before any other signs appear. According to the National Eye Institute, this is the most common type of glaucoma.
narrow-angle (acute) glaucoma
The rapid buildup of fluid if the outflow of water in the eye is suddenly blocked may cause a sharp, rapid, and painful increase in pressure. Narrow angle glaucoma is an emergency. You should contact your doctor immediately if you begin to experience symptoms, such as severe pain, nausea, and blurred vision.
congenital glaucoma
Babies born with congenital glaucoma have a defect in the corner of the eye, which slows or prevents the normal drainage of fluid. Symptoms of congenital glaucoma usually present with blurry eyes, excessive tearing, or sensitivity to light. Congenital glaucoma can run in families.
Secondary glaucoma
Secondary glaucoma often occurs as a side effect of an injury or other eye condition. such as cataracts or eye tumors. Medications such as corticosteroids may also cause this type of glaucoma. In rare cases, eye surgery can cause secondary glaucoma.
Normal tension glaucoma
In some cases, people without high eye pressure develop damage to the optic nerve. This is for an unknown reason. However, severe sensitivity or lack of blood flow to the optic nerve may be an underlying factor in this type of glaucoma.
Who is at risk of developing glaucoma?
Glaucoma is the second leading cause of blindness worldwide, according to the World Health Organization.
Risk factors for glaucoma include:
the age
People over 60 are at risk of developing glaucoma, and the risk of developing glaucoma increases slightly with each year of age. And if you’re African American, your risk starts to increase around age 40
ethnicity
African Americans or people of African descent are more likely to develop glaucoma than Caucasians. People of Asian descent are more likely to develop angle-closure glaucoma, and people of Japanese descent have a higher risk of low-pressure glaucoma.
eye problems
Chronic eye inflammation and thinning corneas can lead to increased pressure in the eyes. Physical injury or trauma to the eye can increase eye pressure.
family history
Some families may run glaucoma genetically. If your father or grandfather had open-angle glaucoma, you’re at increased risk of developing the condition.
Medical history
People with diabetes and those with high blood pressure and heart disease have an increased risk of developing glaucoma.
Use of certain medications
Long-term use of corticosteroids may increase your risk of developing secondary glaucoma.
How is glaucoma diagnosed in the eye?
When diagnosing glaucoma, the ophthalmologist performs a comprehensive eye examination. They’ll check for signs of deterioration, including loss of nerve tissue. They may also use one or more tests and procedures:
Tests to detect glaucoma in the eye
Detailed medical history
Your doctor may want to know what symptoms you’ve been experiencing and whether you have any personal or family history of glaucoma. Doctors will order a general health evaluation to determine if there are other health conditions that may be affecting the health of the eyes, such as diabetes or high blood pressure.
Pressure gauge test
This test is done to measure the pressure inside the eye
Pachymetry test
People with thin corneas are at increased risk of developing glaucoma. It can for the “pachmetery” test
Peripheral test.
Also known as a visual field test. This test tells your doctor if glaucoma is affecting your vision by measuring peripheral or side vision and central vision.
Optic nerve control
If the doctor wants to monitor gradual changes in the optic nerve, he or she may take pictures of the optic nerve to compare the images over time.
Will a patient with glaucoma in the eye become blind?
If the increase in pressure in the eye can be stopped and returned to normal, vision loss can be slowed or even stopped. However, since there is no cure for glaucoma, the patient will likely need treatment for the rest of his life to regulate intraocular pressure. Unfortunately, vision lost as a result of glaucoma cannot be restored.
Can glaucoma (blue water in the eye) be prevented ?
Glaucoma can’t be prevented, but it’s still important to catch it early so you can start treatment that will help prevent it from getting worse. The best way to prevent developing any type of glaucoma early is to have an annual preventive medical appointment. Make an appointment with your ophthalmologist. Simple tests done during routine eye exams may be able to detect damage caused by glaucoma before it progresses and begins to cause vision loss.
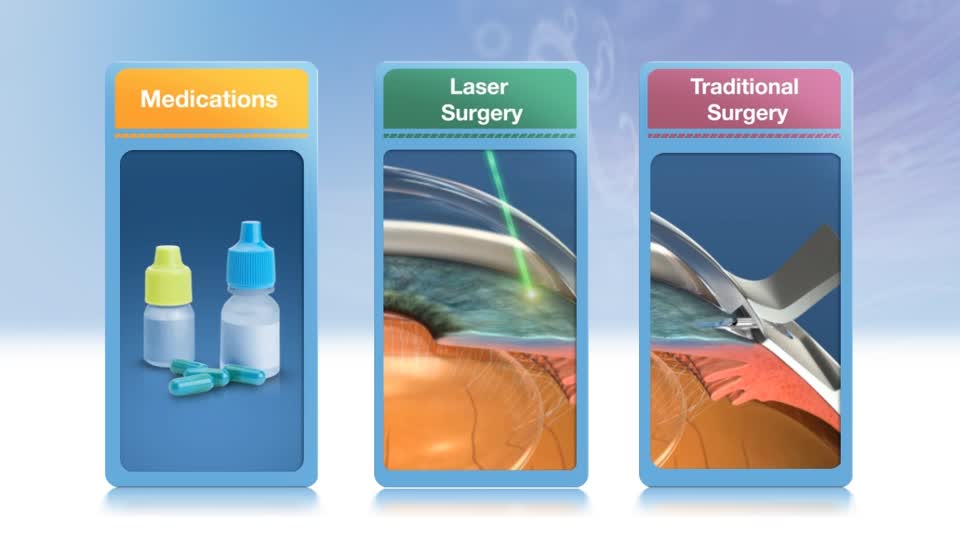
Treatment of glaucoma in the eye
The goal of glaucoma treatment is to reduce eye pressure to stop any further vision loss. Usually, the doctor starts treatment with prescription eye drops. If these treatments don’t work or more advanced treatment is needed, your doctor may suggest one of the following:
Medications for glaucoma in the eye
Several medications designed to reduce eye pressure are available. These medications are available as eye drops or pills, but drops are more common. Your doctor may prescribe one drug or a combination of several.
Glaucoma surgery in the eye
If a partially or completely blocked duct is causing increased eye pressure, your doctor may suggest surgery to create a drainage pathway for the fluid or destroy the tissues responsible for the fluid build-up.
Treatment for angle-closure glaucoma varies. Considering that this type of glaucoma is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment to reduce intraocular pressure as soon as possible. Medicines are usually tried first, to reverse the angle closure, but this may not work. A laser procedure called “ peripheral iridotomy ” can also be performed with a laser. This procedure makes small holes in the iris of the eye to allow for increased fluid movement.
Glaucoma operation in the eye
Surgery isn’t usually the first step in treating glaucoma, but it may preserve your sight if other treatments haven’t worked.
When can glaucoma surgery help?
Your ophthalmologist will give you eye drops or oral medication to lower the pressure in your eye. If medications don’t work, surgery is the next step.
If the medication causes severe side effects such as high blood pressure , a racing heartbeat, or impotence, you may want to try surgery instead.
What are the types of glaucoma surgery?
Doctors may try laser surgery first. You can get treatment at your doctor’s office. You will be able to go home after the operation and return to your normal routine the next day.
A laser is an intense beam of light. It targets your eyes to help open blocked tubes and drain fluids. It may take a few weeks for full results to appear.
What is the treatment of glaucoma in the eye with laser?
Here are some types of laser surgery for glaucoma:
Argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT):
This opens up a blockage in your eye so that fluid can drain. Your doctor may treat half of the blockages first, see how well they work, and then treat the other half later. This method is successful in treating glaucoma in about 75% of people with the most common type of glaucoma.
Selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT):
If ALT is not working well, your doctor may try this technique. Where your doctor applies very targeted low-level laser radiation to places where there is pressure. .
Laser peripheral iridotomy (LPI):
If the distance between the iris (the colored part) and the cornea (the transparent outer layer) is too small, you can develop narrow-angle glaucoma. Where fluid and pressure build up in this area. LPI uses a laser beam to make a small hole in the iris. Excess fluid can drain and relieve pressure.
Ciliary photocoagulation
If other laser treatments or surgery don’t relieve fluid buildup and pressure, your doctor can try this. The laser will beam at a structure inside your eye to relieve pressure. You may need to repeat it over time to keep glaucoma under control.
What do you expect from laser glaucoma surgery?
You can usually have laser surgery done in your doctor’s office or outpatient eye clinic. The doctor will numb your eyes. You should not feel pain during the treatment. You may notice mild stinging or burning.
While you lie still, your doctor will place a special lens over your eye, then aim the laser at the exact spot where you need treatment. It may appear as a very fast and bright flash.
After laser glaucoma surgery
Your vision may be slightly blurred immediately after treatment. You may also feel some pain. Within two hours, the doctor will check your eye pressure. You will need someone to drive you home after surgery.
You may need to continue taking your medications after laser surgery to keep your eye pressure under control.
What are some other types of glaucoma operations?
If laser surgery or medications don’t relieve your eye pressure, you may need a more traditional operation. You may have to go to the hospital or surgery center, and you may need a few weeks to heal and recover.
These procedures include:
Trabeculectomy
The surgeon makes a small cut in the white part of your eye to remove some of the retinal tissue inside. This helps drain excess fluid. You may need to take certain medications along with this surgery so that scar tissue does not form. The procedure can be done in your doctor’s office or on an outpatient basis.
Drainage transplant surgery
The doctor places a small tube inside your eye so that the fluid can drain. Now there are minimally invasive implants.
electrocautery
In this procedure, the surgeon uses a thermal device called a trabectome to make a small cut in the eye’s drainage tubes. It sends heat to the network of tissues inside your eye.
What can you expect after glaucoma surgery?
- You will be given medicines to numb your eyes and make you comfortable. You should not feel any pain. You may feel really sleepy during the procedure.
- After your glaucoma operation, you will rest at home for about a week.
- Do not drive, read, bend over, or lift anything heavy for up to 4 weeks.
- Keep water out of your eyes.
- Your eye may be red, sore, or watery.
- You may also see a small bump at the cut site.
- Also, your vision may be a little blurry for about 6 weeks.
- Contact lenses may not fit until the bump or swelling has gone down.
- About half of the people who have this surgery no longer need medications for pressure
Are there risks from glaucoma surgery?
Glaucoma surgery can make you more likely to develop cataracts later on. Other potential risks include:
- Pain or redness in the eye
- Eye pressure that remains too high or too low
- infection
- inflammation
- bleeding in your eye
Glaucoma surgery cannot restore the sight you have already lost. You may need to take medications or have more surgery in the future if the pressure increases again. Have regular eye exams to make sure you are well.
Glaucoma protection
You cannot prevent glaucoma. But if you find it early, you can reduce the risk of eye damage. These steps may help protect your vision:
- Have regular eye exams. The sooner your doctor detects signs of glaucoma, the earlier you can start treatment. All adults should be screened for glaucoma every 3 to 5 years. If you’re over 40 and have a family history of the disease, get a full eye exam from an ophthalmologist every one to two years. If you have health problems such as diabetes or are at risk for other eye conditions, you may need to go more often.
- Learn about your family history. Ask your relatives if any of them have been diagnosed with glaucoma.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions. If they find that you have high eye pressure, they may give you drops to prevent glaucoma.
- Do moderate activity, such as walking or jogging, at least three times a week.
How can I book for glaucoma surgery in Türkiye?

- Free medical support on the phone: You will have a dedicated representative for your health condition who is always ready to answer your questions.
- Free consultation with a specialist doctor: Your medical representative will consult with a number of doctors and hospitals to find the best possible treatments.
- Free travel visa arrangement: We will contact the embassy in your country to assist you in obtaining a visa to visit Türkiye.
- Free itinerary planning: We will create a schedule for your medical trip to Türkiye.
- Free translation of documents and reports: We will translate medical documents and reports into Turkish on your behalf.
- Free support and monitoring: We will monitor the stages of treatment and be by your side every step of the way.
- Free instant translation: We will be with you during the treatment stages to provide translation between you and the medical team.
- Free accommodation and transportation coordination: We will book accommodation for you and your companions in Türkiye, along with transportation services.
Contact REHABTÜRK doctors for more information about the procedure and to evaluate your medical condition.
