Intra-aortic balloon pump in Türkiye
Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) is a type of therapeutic device. It helps your heart pump more blood. You may need it if your heart can’t pump enough blood for your body.
An IABP consists of a thin, flexible tube called a catheter . Attached to the tip of the catheter is a long balloon. This is called an intra-aortic balloon, or IAB. The other end of the catheter is connected to a computer console. This console contains a mechanism to inflate and deflate the balloon at the right time when your heart beats.
Your heart pumps oxygenated blood and nutrients to all parts of your body. Blood leaves the heart through the arteries, blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood. The outer walls of the heart also contain arteries. These are called coronary arteries. Through these vessels, the heart receives the oxygen and nutrients it needs.
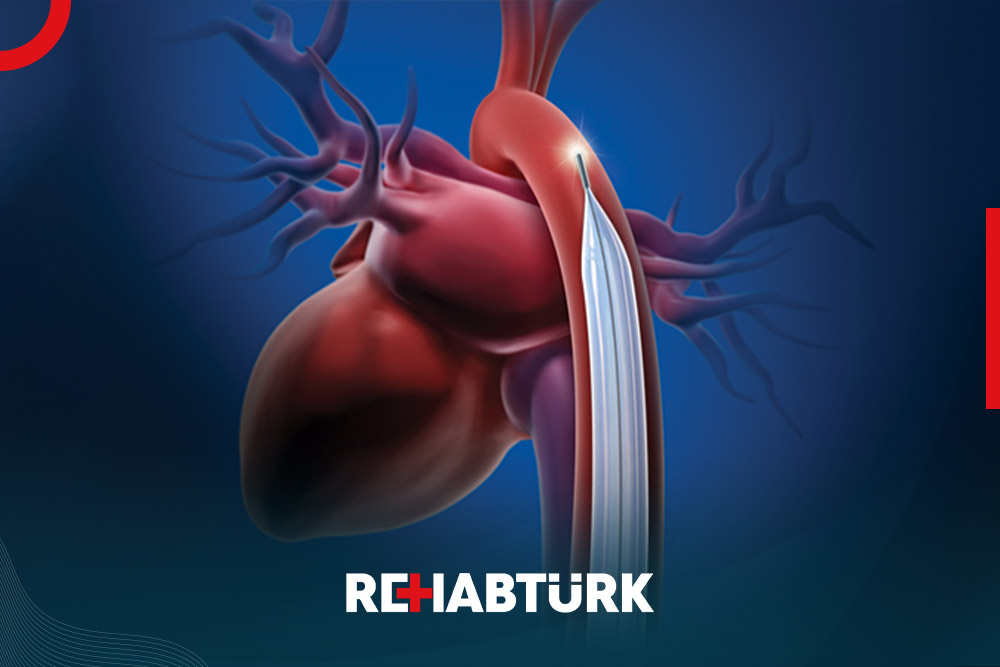
When the heart contracts, it sends blood out to the body. As it relaxes, blood flows into the coronary arteries to bring oxygen to the heart. IABP allows blood to flow more easily into the coronary arteries. It also helps your heart pump more blood with each contraction.
The balloon is inserted into the aorta . The aorta is the very large artery that connects to the heart. In many cases, this procedure is done through a small cut on the inside of your upper leg. Your healthcare provider will insert a balloon pump catheter into an artery in your leg. Then he will direct it to the aorta.
From there, the IABP can start doing its job. The balloon is set to inflate when the heart is relaxed. It pushes blood flow back toward the coronary arteries. You don’t receive enough blood without the pump. When the heart contracts, the balloon deflates. This allows the heart to pump more blood to the body while using less energy. The device continues to swell and deflate until it is removed.
Why might I need pump therapy?
IABP therapy is used to treat cardiogenic shock. This is when your heart can’t pump enough blood to meet your body’s needs.
Some heart problems can cause cardiogenic shock. These include:
- Unstable angina
- heart attack
- Some abnormal heart rhythms
- Heart failure
- heart defects
You may also need an IABP if you have a certain medical procedure. For example, you may need it if you are having a percutaneous coronary intervention. This procedure opens a blocked artery in the heart. You may also benefit from an IABP if you’ve had heart surgery.
In some cases, you may not be able to use an IABP, even if your heart can’t pump enough blood. For example, people with a leaky aortic valve cannot safely use IABP. Those with aortic aneurysms also cannot benefit from treatment.
What are the risks of balloon pump therapy?
Intra-aortic balloon pump therapy can be very helpful. It can sometimes be a life saver. But it does have some risks. These include:
- Damage from decreased blood flow to a limb ( ischemia )
- Artery injury
- Balloon rupture
- Incorrect placement of the balloon, which may cause injury to the kidneys or other problems
- Low platelet count, which can cause excessive bleeding because your blood doesn’t clot as well
- infection
- Apoplexy
Your risks depend on your age and any other medical conditions you may have. For example, a lack of blood flow to your leg is more likely if you have peripheral vascular disease .
How do I prepare for intra-aortic balloon pump treatment?
Before your procedure, talk to your healthcare provider about all of your concerns. He will give you detailed instructions. Be sure to tell your healthcare provider if you are pregnant or think you could be. Also tell him if you have:
- Any other medical conditions
- problem with anesthesia
- New symptoms, such as a sudden fever
If you smoke, you should try to stop before the procedure. This will help reduce your chance of complications. You should also not eat or drink anything after midnight the day of the procedure. You may also need to stop taking any medications. Before and during treatment, you may need to take medicine to help prevent blood clots.
You may need other tests to assess your health beforehand. These may include:
- Baseline blood work (to evaluate for anemia and infection)
- Electrocardiogram (to check heart rhythm)
- a chest X-ray (to see your heart and lungs)
- echocardiogram (to see how well your heart is pumping)
What happens during the installation of the balloon pump?
Intra-aortic balloon pump therapy involves inserting a balloon-tipped catheter into a blood vessel and advancing it to the heart. Usually, this happens during heart-related surgery. In an emergency, a medical team may insert it next to your bed.
Your doctor can tell you exactly what to expect. In general, the procedure contains the following steps:
- You will first receive some anesthesia. If you are having an insertion during surgery, you may already be under general anesthesia. In this case, you will be asleep and not feel anything. In other cases, you may receive medications to help you relax. You will also receive narcotic medications at the insertion site.
- During the procedure, your heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs will be monitored.
- A small cut will be made through an artery in the upper part of the inner thigh. The balloon catheter will be inserted there.
- The surgeon will insert the catheter into a part of your aorta in your chest area. He or she can see this movement using continuous X-ray imaging.
- The balloon will be programmed to inflate when your heart relaxes. You will contract as your heart contracts
- The end of the catheter will be secured, so that it stays in place.
You may feel some pain in the chest after the operation. It should go away within minutes of starting the IABP. If you still have symptoms, you may need further treatment.
Your doctor will monitor you for complications. You will likely need to stay in bed afterward. The head of your bed should be slightly elevated. The leg with the catheter inserted should remain straight. This will help prevent the balloon from moving out of place. You may also need daily chest X-rays to check that the device is still in the correct place. The pump usually makes sounds as it cycles between inflation and deflation.
Tell your doctor right away about any new symptoms, such as bleeding from the insertion site. Chest pain could be a sign that your machine’s timer needs to be adjusted. Paleness or tingling in your leg may indicate decreased blood flow to that area.
What happens after the pump is installed?
You may need to keep the pump on for several days under your doctor’s supervision. He may pause the pump to see how you respond.
If your heart continues to pump well on its own, you may be ready to discontinue IABP therapy. You can also stop treatment when another intervention is available (eg a donated heart).
When it is time to remove the pump, you will likely receive medication to help you relax. Next, the doctor removes the catheter and attached balloon. It will also close the slit on the leg.
Your doctor may recommend additional instructions about what to expect. Follow these instructions carefully to help increase your chances of a positive outcome.
Intra-aortic balloon pump procedure in Türkiye
Many patients come to Türkiye for the balloon pump procedure
REHABTÜRK HEALTHCARE PROVIDER NETWORK treatment services to patients in addition to transportation, accommodation and full trip coordination services.
The balloon pump operation in Türkiye requires an average of about three days for a stay in Istanbul.
Patients receive intensive post-operative care to check their condition and satisfaction after the intra-aortic balloon pump procedure. In addition, our patient support team is available 24/7.

