Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a medical method in which doctors examine, diagnose, and resolve issues occurring within a joint through surgery. This procedure is considered to be minor and can be done as an outpatient, allowing patients to return home on the same day. Your doctor may suggest arthroscopy if you are experiencing joint inflammation, have sustained a joint injury, or have gradually incurred joint damage.
What are the types of arthroscopy?
Surgeons utilize arthroscopy as a means to observe the inside of joints without the need for extensive surgical cuts. Various forms of arthroscopy are available.
- Elbow arthroscopy.
- Foot and ankle arthroscopy.
- Hand and wrist arthroscopy.
- Hip arthroscopy.
- Knee arthroscopy.
- Shoulder arthroscopy.
How to prepare for the procedure
Consult your physician to inquire about the advantages and potential drawbacks associated with arthroscopy as a treatment option for your specific condition. Prior to consenting to the procedure, it is advisable to explore alternative choices and discuss them with your doctor.
- losing weight
- pain relief
- anti-inflammatory medication
- exercise
- physiotherapy
Prior to performing an arthroscopy, the doctor will assess the joint by requesting x-rays, MRI scans, or other types of imaging. In addition, they may also conduct blood tests or other examinations.
If you decide to proceed with the surgery, you may be requested to stop smoking (in case you are a smoker) and lose weight (if you are considered overweight). Additionally, it may be necessary for you to discontinue certain medications, but it is important to consult your doctor before discontinuing any medications.
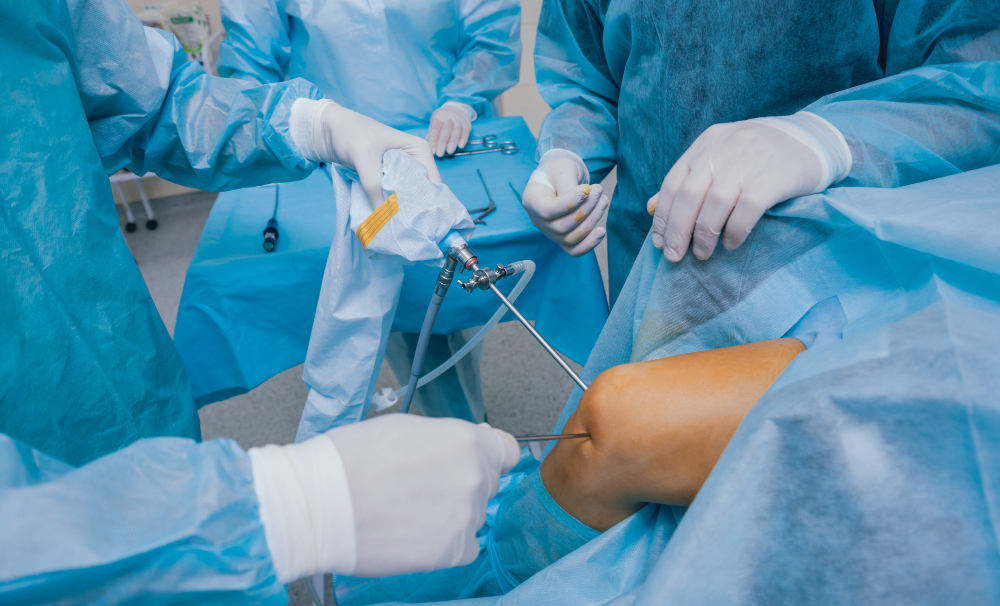
What Happens During the Procedure?
In a hospital or outpatient operating room, your doctor will carry out arthroscopic surgery. The specific anesthesia you will be given during the procedure will be determined by the joint being treated and the suspected issue identified by your surgeon. This could involve general anesthesia, where you will be asleep during the surgery, or anesthesia administered through your spine. Additionally, the surgical area may be numbed by the doctor.
In order to examine the joint, the doctor will use narrow instruments and carefully place them through a small incision that is as wide as a buttonhole. The instrument, known as an arthroscope, includes a camera lens and a light to provide visual access to the joint. The camera will display the joint’s image on a screen. Additionally, the surgeon will introduce sterile fluid into the joint to expand it, facilitating better visibility.
The joint will be examined, the issue will be identified, and the necessary surgical procedure, if required, will be determined. If surgery is necessary, the surgeon will use specific instruments through small incisions called portals. These instruments will be used to remove, shape, hold, and secure stitches into the bone.
In the event that your surgeon determines that you require conventional, “open” surgery to address the issue, they might choose to perform it concurrently with your arthroscopic surgery.
Later on, the arthroscope and its accompanying accessories will be taken out. The wound will then be sealed using either specialized tape or stitches.
What happens after arthroscopy?
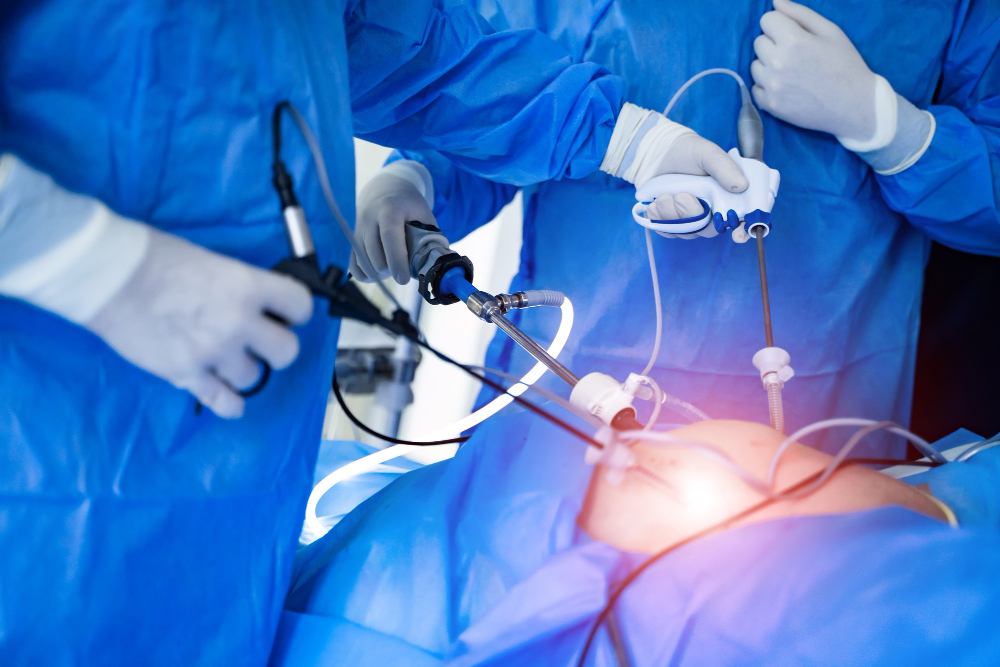
After the procedure, it is possible for you to return home in just a few hours. It might be necessary for you to:
- For a certain period of time, it is advisable to refrain from putting any weight or exerting pressure on the affected area. In the case of undergoing hip or leg arthroscopy, it may be necessary to rely on crutches or other devices to aid in mobility.
- Ice and elevate the area.
- Keep the incision clean and covered.
- Take NSAIDs for pain.
- It is recommended to have showers instead of baths until the cut has fully healed.
- Wear a sling or brace.
Recovering from an arthroscopy
The complete recovery process after an arthroscopy can vary, ranging from approximately one week to several months.
The outcome can vary based on various factors.
- For instance, the recovery period for a knee arthroscopy is generally longer compared to a wrist arthroscopy when considering the affected joint.
- Did you receive any medical procedures, such as joint repair, during your arthroscopy?
- your general state of health
The employees at the arthroscopy department will provide you with more specific details.
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES?
Compared to the conventional open surgery, arthroscopy is a less invasive procedure. This allows certain surgeries to be done on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day. Arthroscopy can also decrease pain and the requirement for pain medication after surgery, while also reducing the overall recovery period.
Conditions
Some of the conditions that are often addressed through arthroscopic procedures include:
- Inflammation is a common occurrence in various parts of the body, causing swelling and discomfort. One specific example is synovitis, which is characterized by inflamed tissues surrounding joints such as the knee, shoulder, elbow, wrist, and ankle.
- Acute or chronic injuries, including:
- Rotator cuff tendon tears
- Shoulder impingement
- Recurrent dislocation in the shoulder
- Meniscal (cartilage) tears in the knee
- Chondromalacia refers to the deterioration or damage of the cartilage cushion in the knee.
- Knee instability is often caused by tears in the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL).
- Carpal tunnel syndrome in the wrist
- Loose bone and/or cartilage fragments, specifically in the knee, shoulder, elbow, ankle, or wrist.
Treatment in Türkiye:
The medical staff of surgical teams, doctors and consultants in Rehab Türk can provide the best treatment options and free consultations – by striving to keep abreast of the latest medical technologies and methods.

