Deep brain stimulation in Türkiye
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure based on implanting electrodes in specific areas of the brain that generate electrical impulses that control abnormal brain activity. Programmable and placed under the skin in the upper chest.
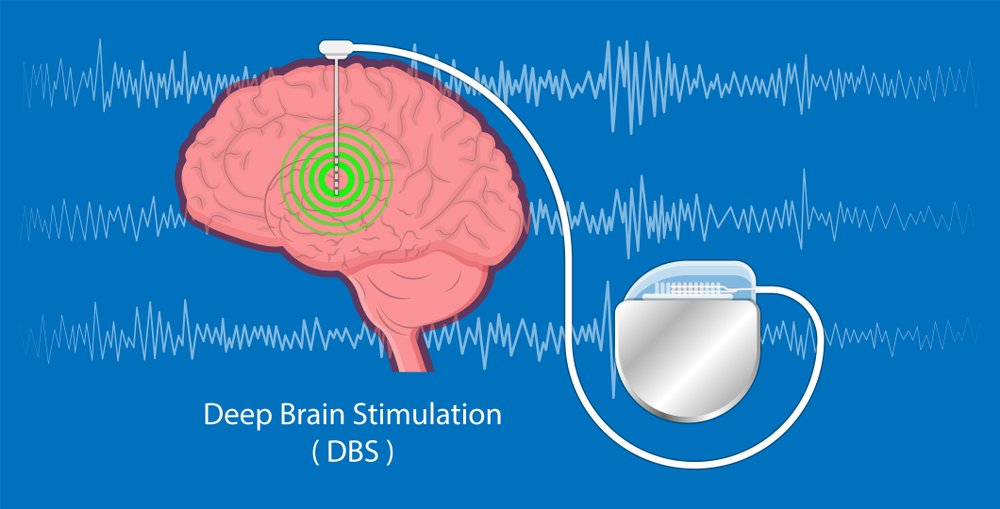
The deep brain stimulation system has three components:
- Electrode: A thin, insulated wire is inserted through a small hole in the skull and implanted in a specific area of the brain.
- Extension cord: connects the electrode to the internal pulse generator and is passed in isolation under the skin of the head, neck and shoulder.
- IPG Internal Pulse Generator: These are implanted under the skin in the upper chest.
Conditions treated using deep brain stimulation are:
- muscle dystonia.
- Epilepsy.
- tremor.
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder.
- Parkinson’s disease.
- Depression
These diseases affect hundreds of thousands of people worldwide.
Pathological causes:
Deep brain stimulation is used to treat patients with movement disorders such as idiopathic tremor, Parkinson’s disease, and muscular dystonia. It is also used to control symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder and epilepsy. This type of surgical treatment is resorted to when drugs become ineffective for the previous category of patients. Deep brain stimulation is used in Treating more than 160,000 people with various neurological conditions.
Pathological symptoms:
Specific symptoms appear for each patient individually, but the most common symptoms are:
Dystonia:
- Involuntary muscle contractions occur during certain activities (such as typing).
- Muscle spasms that get worse with stress, fatigue, or anxiety.
Epilepsy:
- temporary confusion.
- A staring spell.
- Unconsciousness.
- Uncontrollable tremor of the arms or legs.
- Emotional responses such as fear, anxiety.
Deep brain stimulation in the treatment of tremor:
Tremor that occurs during daily activities such as writing or drinking.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder:
- Fear of germs or contamination.
- Aggressive thoughts towards others or towards oneself.
- Obsession with symmetrical and perfect arrangement of things.
- Excessive cleaning or hand washing.
- compulsive counting.
- Frequently checking objects (such as checking the oven, door, etc.).
Parkinson’s disease:
- tremor.
- Slow or slow movement.
- tetanus.
- Abnormal walking.
Parkinson’s disease:
Tremor, stiffness, and slowness of movement result from the death of dopamine-producing neurons responsible for transmitting messages that control body movement.
Tests and Diagnosis:
The affected patients are diagnosed through a multidisciplinary medical team consisting of a neurologist, a neurosurgeon, a neuropsychiatrist and a psychiatrist. Patients with Parkinson’s disease or Parkinson’s disease are subjected to tests for motor symptoms while they are taking medications and while they are free of them, in order to assess the severity of the disease. Also, tests for epilepsy patients include electroencephalography and tests Some patients may undergo a neuropsychological evaluation, and obsessive-compulsive disorder patients complete the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale test.
Prior to deep brain stimulation surgery, patients undergo the following:
- Blood and urine tests (helps to identify toxins, etc.).
- MRI and/or CT scans (this helps target the right area of the brain to relieve symptoms).
- Medical clearance.
Candidates for deep brain stimulation meet these criteria:
- Symptoms significantly reduce quality of life.
- Symptoms cannot be controlled despite receiving an adequate dose of medication.
- Side effects from current medications are not tolerated.
treatment:
Non-surgical treatments:
Doctors first resort to trying treatments such as medication and physical therapy before considering surgical interventions, such as deep brain stimulation.
Surgical treatments:
Its advantages:
- It can be performed on one or both sides of the brain, depending on the symptoms.
- The effects are reversible and individually customized depending on each patient’s clinical condition.
- Stimulation settings can be modified to reduce potential side effects and improve efficacy over time.
- The device provides continuous symptom control 24 hours a day.
- Participation in other therapies such as stem cell or gene therapy.
Before deep brain stimulation surgery:
- The patient gives his medical history including allergies, medications, anesthesia reactions, and previous surgeries.
- Stop taking all nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (IBUPROFEN, NAPROXEN) as well as blood thinners (COUMADIN, ASPIRIN, PLAVIX) seven days before surgery.
- Not drinking alcohol and using nicotine one week before and two weeks after surgery, in order to avoid bleeding and problems with the healing process.
- It is required to wash skin and hair with Hibiclens or a special soap prior to surgery.
- No food or drink is allowed the night before the surgery.
During deep brain stimulation surgery:
The entire DBS process takes 5 to 7 hours. The surgery takes 3 to 4 hours, and the first step begins with placing a stereotaxic frame on the patient’s head temporarily using Velcro Straps. The four pin sites are injected with local anesthesia, then a mild sedative is administered. One inch wide hair is shaved along the incision line. A skin incision is made across the top of the head, and two holes are opened on the left and right sides of the skull using a drill, through which an electrode enters the brain to a specific and planned location inside the brain.
After that, a number of tests are conducted, such as raising the arms or legs, or counting numbers, and the brain cell activity is displayed on the computer and the exact location of the neurons is determined. Then a plastic cover is placed over the hole to fix the electrode in place, and a file of wire is left under the scalp to tie it. Later with an extension cord and stimulator, and finally the scalp incision is closed with sutures and a bandage is applied. And the deep brain stimulation process ends.
After deep brain stimulation surgery:
The patient stays in the hospital for monitoring and observation, then returns home the next day. After about a week, he returns to the hospital to undergo surgery to implant the stimulator in the chest. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia and takes about an hour. Patients return home on the same day.
Stimulator implant surgery:
Part of the scalp incision is reopened to access the electrical leads, then a small incision is made near the collarbone, the neurostimulator device is implanted under the skin, and then connected to an extension cord that is passed under the skin of the scalp down the neck and then to the stimulator in the chest
Catalyst programming:
The stimulator is programmed about 10 days after deep brain stimulation surgery and the drug dose is adjusted accordingly. It is reprogrammed through 3 to 4 sessions every 3 weeks to achieve maximum control of symptoms while minimizing side effects. Most people do not feel the stimulation because it reduces their symptoms, but some may feel People with a brief tingling sensation when they first turn on the catalyst
Risks:
The treatment has potential but minor and reversible risks and side effects, and deep brain stimulation is safe and effective in properly selected patients.
Risks include:
- The risk of cerebral hemorrhage, including stroke, is 1%.
- infection.
- A malfunction in the machine.
- No benefit for certain symptoms.
- headache.
- Deterioration of mental or emotional condition.
Side effects during stimulation include:
- Temporary tingling in the face or extremities.
- A feeling of tightness in the muscles.
- Speech or vision problems.
- Loss of balance.
Deep brain stimulation in Türkiye
The medical staff of surgical teams, doctors and consultants in REHABTÜRK can provide the best treatment options and free consultations – by striving to keep abreast of the latest technologies and medical methods.
