Laser Photocoagulation , Expectations Uses, Recovery
Laser photocoagulation is a surgical procedure for the eyes that uses laser heat to shrink or eliminate abnormal blood vessels in the retina. It is a treatment for age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a condition that can lead to vision loss.
Why the Procedure is Performed
Diabetes can affect the eyes through a condition known as diabetic retinopathy, which often requires laser photocoagulation. Diabetic retinopathy is a common eye disease that can harm the retina, the back part of the eye. The most severe form of diabetic retinopathy is proliferative diabetic retinopathy, where abnormal blood vessels grow on the retina. These vessels can lead to bleeding or scarring over time.
In laser photocoagulation treatment for diabetic retinopathy, laser energy is directed at specific areas of the retina to prevent the growth of abnormal vessels or to shrink existing ones. At times, the procedure is performed to eliminate fluid buildup (edema) in the central part of the retina, known as the macula.
Laser Photocoagulation Uses
Laser photocoagulation is a versatile method used to treat various eye conditions. Some common conditions it can address include:
Diabetic retinopathy, a complication of diabetes, can cause abnormal blood vessels to grow in the eye, leading to swelling and leakage. Laser photocoagulation helps seal these vessels, preventing further growth and safeguarding vision. However, it may affect color perception and night vision.
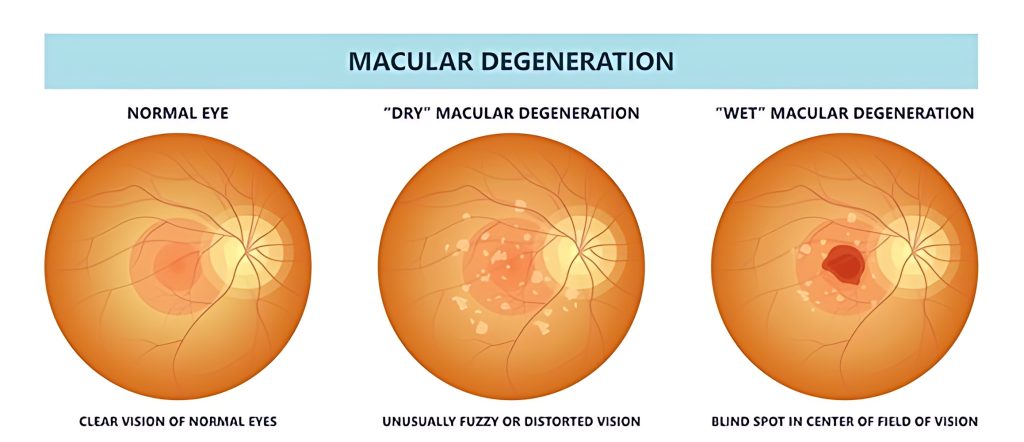
Macular degeneration is a condition that affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. There are two types of age-related macular degeneration: dry and wet. The wet type is more severe and can cause leakage from abnormal blood vessels, threatening the macula. Laser photocoagulation is used for severe cases to seal off these vessels. However, it is less effective for scattered vessels or those in the central macula. Other treatments such as medications can slow abnormal blood vessel growth.
Retinoblastoma is an eye cancer that starts in the retina, often in infants and children. Laser photocoagulation targets and destroys blood vessels around the tumor. It is suitable for small tumors in the back of the eye.
Retinal Detachment: Retinal detachment occurs when the retina pulls away from its normal position, posing a serious threat to vision.Laser photocoagulation creates a scar near the detachment, helping the retina reattach to the tissue.
Retinal Tear: A retinal tear is a rip in the retina, causing blurry vision and potentially leading to detachment. Photocoagulation stops fluid flow beneath the retina, preventing retinal detachment.
Laser photocoagulation is invaluable for these conditions, offering targeted treatment to preserve vision and address specific eye issues.
What to expect during the procedure
Laser photocoagulation is a minimally invasive outpatient technique, typically carried out in an ophthalmology office or clinic. The procedure, lasting less than half an hour, is relatively painless. Since it’s non-invasive, patients can return home shortly afterward, although driving is not advisable. It is important to arrange for someone to accompany you and drive you home.
In general, the procedure involves the following steps:
- Explanation of the procedure by your eye doctor.
- Application of numbing and dilating eye drops.
- Placement of your chin in a chinrest with your eyes focused ahead or on a target.
- Positioning a focusing lens on the eye to be treated.
- Administering laser treatment pulses to the targeted area of the retina.
- Application of eye drops to prevent inflammation.
During the laser treatment, you might see flashes of light or experience mild sensations, but your eye doctor will ensure your comfort. After the procedure, during the one or two-day recovery period, you might encounter slight discomfort or mild eye pain. A follow-up appointment a few days later will allow your doctor to monitor your healing progress.
The number of necessary sessions depends on your eye condition and its severity. Your eye doctor will assess your progress to determine the required number of sessions. This may entail follow-up appointments for weeks or months after the initial session.
Most individuals, depending on the condition treated, can usually resume their normal routines within a day or two. However, if treating a retinal hole or tear, the eye doctor might recommend restricting activities for one or two weeks.
After the Procedure
Your vision will be blurry for the first 24 hours. You may see floaters, but these will go away over time. If your treatment was for macular edema, your vision may seem worse for a few days.
Summary
laser photocoagulation is an eye surgery utilizing lasers to eliminate abnormal blood vessels, preventing additional vision loss. Retina specialists employ this procedure to treat various eye diseases like diabetic retinopathy and retinal detachment. Possible risks include developing a new blind spot and experiencing diminished color or night vision. The process typically involves using eye drops to dilate the pupils, followed by laser treatment.
Treatment in Türkiye:
The medical staff of surgical teams, doctors, and consultants at REHABTÜRK can provide the best treatment options and free consultations, striving to stay up-to-date on the latest medical technologies and methods.

