Oral cancer treatment in Türkiye
mouth cancer
Oral cancer is cancer of the tissues of the mouth or throat. It belongs to a larger group of cancers called head and neck cancers. Most develop in the squamous cells of the mouth, tongue, and lips.
It most often occurs in people over the age of 40. Oral cancers are often discovered after they have spread to the lymph nodes in the neck. Early detection is the key to surviving oral cancer.
Types of oral cancers
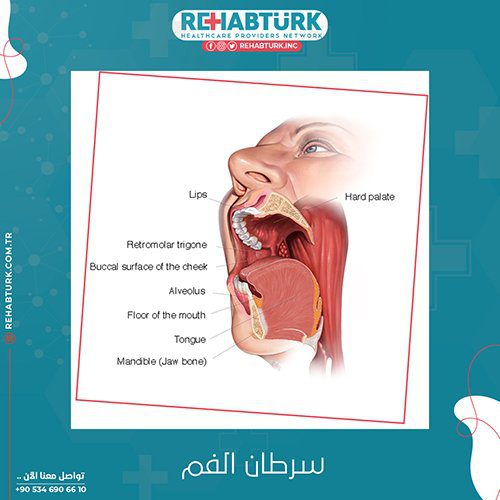
Oral cancers include cancers of:
- lips
- the tongue
- The inner lining of the cheek
- gums
- floor of the mouth
- Hard and soft palate
The dentist is often the first healthcare provider to notice signs of oral cancer . Having semi-annual dental exams can keep your dentist updated on your oral health.
Risk factors for oral cancer
Tobacco use is one of the biggest risk factors for oral cancer. This includes smoking cigarettes, cigars, and pipes, as well as chewing tobacco.
People who consume large amounts of alcohol and tobacco are at greater risk, especially when they use both products on a regular basis.
Other risk factors include:
human papilloma virus ( HPV ) infection
Chronic exposure to sunlight on the face
A previous diagnosis of oral cancer
A family history of oral cancer or other types of cancer
Weakened immune system
Malnutrition
Genetic syndromes
Men are more likely to get oral cancer.
What are the symptoms of oral cancer?
Symptoms of oral cancer include:
- A sore that does not heal in the lips or mouth
- A lump or growth anywhere in the mouth
- Bleeding from the mouth
- Loose teeth
- Pain or difficulty swallowing
- Trouble wearing dentures
- a lump in the neck
- Constant earache
- Significant weight loss
- Numbness in the lower lip, face, neck, or chin
- White, red, white, or red patches in or on the mouth or lips
- sore throat
- Pain or stiffness in the jaw
- tongue pain
How is oral cancer diagnosed?
First, the doctor or dentist will perform a physical examination. This includes a careful examination of the roof and floor of your mouth, the roof of your mouth, tongue, cheeks, and lymph nodes in the neck. If the doctor cannot determine the cause of the symptoms, a referral may be made to an ear, nose and throat specialist.
If the doctor finds any suspicious tumors or lesions, he or she will perform a brush biopsy or tissue biopsy. A brush biopsy is a painless test that collects cells from a tumor by brushing them onto a slide. A tissue biopsy involves removing a piece of tissue so that it can be examined under a microscope for cancer cells.
In addition, the doctor may perform one or more of the following tests:
- X-rays to see if cancer cells have spread to the jaw, chest, or lungs
- A CT scan to check for any tumors in the lobe, throat, neck, lungs, or elsewhere in the body.
- A PET scan to determine if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or other organs.
- MRI scan to show a more accurate picture of the head and neck and to determine the extent or stage of the cancer.
- Endoscopy to examine the nasal passages, sinuses, inner throat, and trachea.
What are the stages of oral cancer?
There are four stages of oral cancer.
Stage I : The tumor is 2 centimeters (cm) or smaller, and the cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes.
Stage II : The size of the tumor is between 2-4 cm and the cancer cells have not spread to the lymph nodes.
Stage III : The tumor is either larger than 4 cm and has not spread to the lymph nodes, or of any size and has spread to one lymph node, but not to other parts of the body.
Stage IV : Tumors of any size and cancer cells have spread to nearby tissues, lymph nodes, or other parts of the body.
According to the National Cancer Institute, the five-year survival rates for cancer of the oropharyngeal cavity are as follows:
83% for localized cancer (that has not spread).
64% for cancer that has spread to nearby lymph nodes
38%, for cancer that has spread to other parts of the body
Overall, 60% of all people with oral cancer will live for five years or longer. The earlier the stage of diagnosis, the greater the chance of survival after treatment. In fact, the five-year survival rate for people with stage I and II oral cancer is 70 to 90 percent. This makes timely diagnosis and treatment even more important.
How is oral cancer treated?
Oral cancer treatment varies according to the type of cancer, its location, and the stage at diagnosis.
surgery
It usually involves surgery to remove the tumor and the cancerous lymph nodes. In addition, other tissues around the mouth and neck may be removed.
radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is another option. This involves aiming radiation beams at the tumor once or twice a day, five days a week, for two to eight weeks. Treatment for advanced stages usually includes a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a treatment with drugs that kill cancer cells. The drug is given either by mouth or through an IV line. Most people receive chemotherapy on an outpatient basis, although some require hospitalization.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is another form of treatment. It can be effective in both early and advanced stages of cancer. Targeted therapies bind to certain proteins on cancer cells and interfere with their growth.
nutrition
Nutrition is also an important part of oral cancer treatment. Many treatments cause difficulty and pain while eating and swallowing, and poor appetite and weight loss are common. Therefore, the diet should be discussed with the doctor.
Getting expert nutrition advice can help you plan a menu that is gentle on the mouth and throat, and provides the body with the calories, vitamins and minerals it needs to heal.
Maintaining oral health
Finally, maintaining oral health during cancer treatment is an important part of treatment. Make sure to keep your mouth moist and clean your teeth and gums.
Recovering from oral cancer treatment
Healing is different from each type of treatment. Postoperative symptoms can include pain and swelling, but removal of small tumors is usually not associated with long-term problems.
Removing large tumors may affect the ability to chew, swallow, or speak as before surgery. The patient may also need reconstructive surgery to reconstruct the bones and facial tissues that were removed during surgery.
Radiation therapy can have a negative effect on the body. Some of the side effects of radiation include:
- Sore throat or mouth
- Dry mouth and loss of salivary gland function
- tooth decay
- Vomiting and nausea
- Inflammation or bleeding gums
- Skin and mouth infections
- Jaw stiffness and pain
- Problems wearing dentures
- fatigue
- Change in the ability to taste and smell
- Changes in the complexion, including dryness and burning
- Weight loss
- Thyroid changes
Chemotherapy drugs can be toxic to rapidly growing non-cancerous cells. This can cause side effects such as:
- hair loss
- Pain in the mouth and gums
- bleeding in the mouth
- severe anemia
- Weakness
- Poor appetite
- Nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- Mouth and lip ulcers
- Numbness in the hands and feet
Recovery from targeted therapies is usually minimal. Side effects of this treatment can include:
- fever
- Headache
- vomiting
- Diarrhea
- allergic reaction
- rash
Although these treatments have side effects, they are often necessary to defeat cancer. Your doctor will discuss side effects and help you weigh the pros and cons of treatment options.
Reconstruction and rehabilitation after oral cancer treatment
People diagnosed with advanced oral cancer will likely need reconstructive surgery and some rehabilitation to help with eating and talking while they recover.
Reconstruction may include dental implants or grafts to repair lost bone and tissue in the mouth or face. An artificial palate is used to replace any missing tissue or teeth.
Rehabilitation is also necessary for advanced cancer cases. Speech therapy can be provided from the time of discharge from surgery until the maximum level of improvement is reached.
How can I book for oral cancer treatment in Türkiye?

- Free medical support on the phone: You will have a dedicated representative for your health condition who is always ready to answer your questions.
- Free consultation with a specialist doctor: Your medical representative will consult with a number of doctors and hospitals to find the best possible treatments.
- Free travel visa arrangement: We will contact the embassy in your country to assist you in obtaining a visa to visit Türkiye.
- Free itinerary planning: We will create a schedule for your medical trip to Türkiye.
- Free translation of documents and reports: We will translate medical documents and reports into Turkish on your behalf.
- Free support and monitoring: We will monitor the stages of treatment and be by your side every step of the way.
- Free instant translation: We will be with you during the treatment stages to provide translation between you and the medical team.
- Free accommodation and transportation coordination: We will book accommodation for you and your companions in Türkiye, along with transportation services.
Contact REHABTÜRK doctors for more information about the procedure and to evaluate your medical condition.

