Neuroendocrine Tumors
Neuroendocrine tumors are a type of tumor that starts in specific cells of the neuroendocrine system and is not very common. In the past, it was considered a rare cancer and was sometimes not detected. However, with the availability of more advanced medical tests, healthcare providers can now diagnose neuroendocrine tumors more accurately and quickly. This has led to earlier treatment and an increased number of individuals surviving with neuroendocrine tumors for many years.
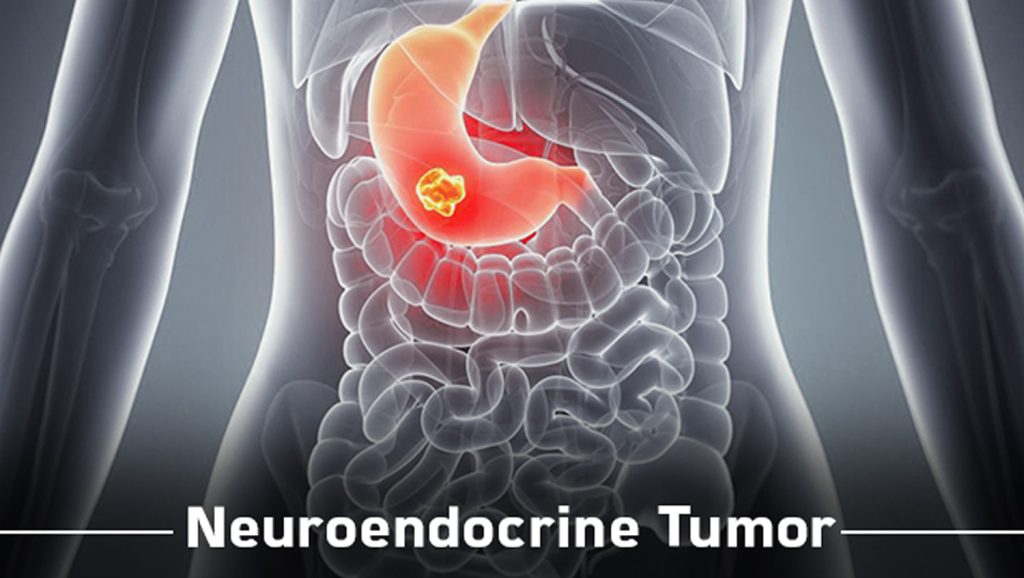
What are neuroendocrine tumors, and where are they usually found?
Although the term “neuroendocrine” suggests that these tumors affect both nerve cells and hormones, they are primarily assumed to originate from endocrine cells. The inclusion of “neuro-” in the name is more of a historical curiosity.
Essentially, neuroendocrine tumors are malignant growths that may occur in any location with endocrine cells. These cells play a crucial role in controlling bodily processes, including metabolism, reproduction, and growth. While they are present throughout the body, the lungs, small intestines, and pancreas typically have the highest incidence of tumor development.
Symptoms of neuroendocrine tumors
The indications of a neuroendocrine tumor vary according to the part of the body it is located in and the specific hormones it generates.
To illustrate, a type of cancerous growth in the digestive tract called gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumour can bring about symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, or abdominal discomfort.
A growth in the lung called pulmonary neuroendocrine tumour can lead to wheezing or an ongoing cough.
Certain growths can result in excessive quantities of hormones entering the bloodstream, dubbed “functioning tumors,” which may produce symptoms like diarrhea, warmth and redness in the face and neck, spasms, breathing difficulties, low blood sugar, fluctuations in blood pressure, and heart issues.
When to see a doctor
Arrange a meeting with your physician in case you experience continuous indications or indications that concern you.
Which varieties of neuroendocrine tumors exist?
Neuroendocrine tumors are categorized as either primary or secondary tumors. Primary tumors refer to cancer that has not yet metastasized to other body parts. Secondary tumors, on the other hand, pertain to NETs that have already spread out, often affecting the lymph nodes in your lymphatic system, bones, or liver.
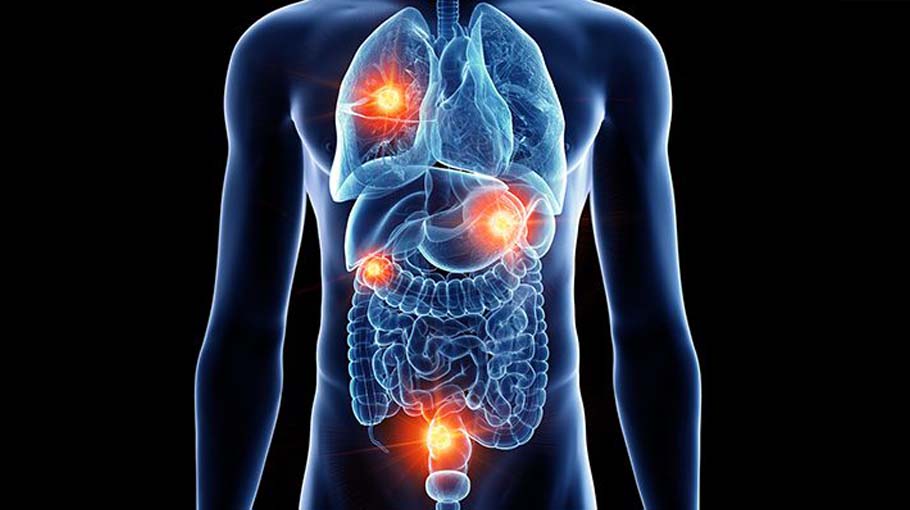
The category of NETs is determined by where they are located. For instance, if a neuroendocrine tumor is present in the digestive system, it is referred to as a neuroendocrine tumor of the gastrointestinal tract. The main types of primary neuroendocrine tumors are listed below.
- NETs (neuroendocrine tumors) usually occur in the GI tract, with the large intestine being the most common site (20%), followed by the small intestine (19%) and appendix (4%). The GI tract is responsible for breaking down food and liquid and disposing of waste. These tumors were previously referred to as carcinoid tumors.
- The bronchial system, responsible for air transport to the lungs, is where approximately 30% of NETs can be found. This makes the lung the second most frequent location for NETs to appear. These tumors were previously referred to as carcinoid tumors.
- Around 7% of NETs can emerge in the pancreas, an organ shaped like a pear situated in the abdominal region between the backbone and the stomach. PNETs (Pancreas NETs), previously known as islet cell tumors, make up about 7% of all pancreatic cancers.
How are neuroendocrine tumors treated?
Surgery
For patients with localized NETs, the typical initial recommendation is to surgically remove the primary tumor. The aim of the surgery is to fully eliminate the neuroendocrine tumor or decrease its size. In cases where the disease is advanced, surgery may be considered to alleviate symptoms. Different surgical techniques for NETs are available, including minimally invasive laparoscopic resections, debulking or cytoreductive surgery, and liver transplantation.
- Enucleation is a surgical procedure that solely removes the tumor and is typically recommended for small and confined tumors.
- If it is not possible to remove the entire tumor, reducing its size through debulking surgery could be considered. This type of surgery may alleviate certain symptoms associated with an NET.
- Cytoreductive surgery is a procedure in which gastrointestinal NETs are operated upon, with the aim of eliminating as many cancerous cells as possible and thereby limiting the production of hormones by the tumor. This type of surgery might also alleviate some of the symptoms triggered by the tumor.
- Laparoscopic surgery is a less invasive technique for removing cancerous cells in the abdomen using only one or a few small incisions. This type of surgery has the advantage of a quicker recovery time compared to standard surgery.
- When neuroendocrine tumors have metastasized to the liver, it is possible to consider a liver transplant as a method of treatment.
- If a tumor cannot be completely extracted from the body, it is possible to perform a palliative surgery that aims to decrease symptoms by reducing the size of the tumor. The main objective of this type of surgery is to enhance comfort and improve the overall quality of life of the patient. Palliative surgery can be combined with radiation therapy to achieve better outcomes.

Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy may be employed as a solitary form of treatment or in conjunction with other therapies for NETs. Its usage primarily occurs when symptoms arise or the growth has spread. Several chemotherapy drugs, all of which impede the expansion and duplication of cancer cells, are available. If the illness has reached the liver, chemoembolization, whereby chemotherapy medications are administered directly into the tumor, may be a feasible alternative. During the chemotherapy treatment regimen, patients may encounter adverse reactions like:
- Hair loss
- Reduced appetite
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
How can I reduce my risk?
Scientists are unsure about the reason that triggers the excess growth of neuroendocrine cells leading to the formation of tumors. Inherited conditions have been associated with the development of NETs. Consult your medical professional for assistance in comprehending about hereditary conditions and if your family’s medical history makes you susceptible to NETs.
A note from rehabturk
Being diagnosed with NET could be somewhat comforting as it could put an end to the years of perplexity of trying to determine the reason behind not feeling well. However, realizing that you are suffering from a rare and severe ailment might replace some of the uncertainties with new ones. Having a discussion with your health care provider regarding the diagnosis of NET and the plan of treatment may help you regain confidence and manage your health better.
Treatment in Türkiye:
The medical staff of surgical teams, doctors and consultants in REHABTURK can provide the best treatment options and free consultations – by striving to keep abreast of the latest medical technologies and methods.

