Pancreatic cancer treatment in Türkiye
What is pancreatic cancer?
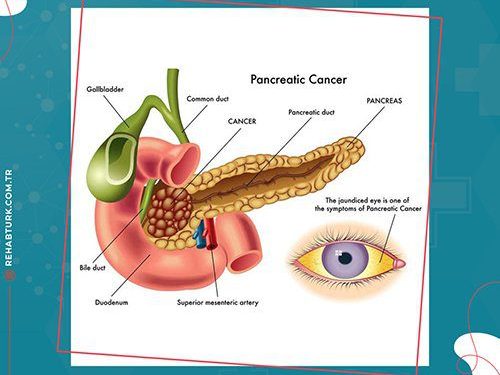
Pancreatic cancer occurs within the tissues of the pancreas. It is a vital endocrine organ located behind the stomach. The pancreas plays an essential role in digestion by producing the enzymes the body needs to digest fats, carbohydrates and proteins. The pancreas also produces two important hormones “glucagon and insulin.” These hormones are responsible for controlling blood sugar (glucose) metabolism. Insulin helps cells metabolize sugar for energy and glucagon helps raise glucose levels when they are too low. Because of the location of the pancreas, pancreatic cancer can be difficult to detect and is often diagnosed at more advanced stages of the disease.
Symptoms of pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer often does not show symptoms until it is in the advanced stages of the disease. This is why there are no early signs of pancreatic cancer. Even once the cancer has grown, some of the most common symptoms can be subtle
- Anorexia
- Unintentional weight loss
- Abdominal (stomach) or lower back pain
- blood clots
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- gloom
Pancreatic cancer may worsen pre-existing symptoms if the cancer spreads, and additional signs and symptoms of advanced pancreatic cancer may be present.
Causes of pancreatic cancer
The cause of pancreatic cancer is not yet known. This type of cancer occurs when abnormal cells begin to grow and form tumors within the pancreas. An increasing amount of abnormal cells are produced and these cells eventually take over the healthy cells.
In fact, doctors and researchers do not know what causes changes in cells, but they do know some common factors that may increase a person’s risk of developing this type of cancer. The two most important risk factors are inherited genetic mutations and acquired genetic mutations. Genes control the way these cells function, so changes in these genes can lead to cancer.
Pancreatic cancer survival rate
The survival rate is the percentage of the number of people with the same type and stage of cancer who are still alive after a specified period of time.
This number does not indicate how long people may live, instead it helps measure how well cancer treatment is working. Many survival rates are stated as a five-year percentage. These survival rates are not definitive
The five-year survival rate for those with localized pancreatic cancer is 34% for those with localized pancreatic cancer stage 0, 1, and 2 and the five-year survival rate for “regional” pancreatic cancer that has spread to nearby structures or lymph nodes is 12% within Phases 2 and 3
Metastatic pancreatic cancer or stage 4 cancer that has spread to other sites such as the lungs, liver or bones has a survival rate of 3%
Stages of pancreatic cancer
When pancreatic cancer is detected, doctors will likely order additional tests to see how far and where the cancer has spread. Imaging tests, such as a positron emission tomography (PET) scan, help doctors determine the presence of cancerous tumors. Blood tests may also be used. Through these tests, doctors try to determine the stage of the cancer, and this helps explain the extent of the cancer’s progress and determine treatment options. Once a diagnosis is made, the doctor will determine the stage of the cancer based on the test results. The stages of pancreatic cancer are divided into the following:
- The first: tumors found in the pancreas only
- The second: spread of tumors to the abdominal tissues or nearby lymph nodes
- Third: the spread of cancer to the main blood vessels and lymph nodes
- Fourth: the spread of tumors to other organs such as the liver
Stage IV pancreatic cancer
At this stage, it begins to spread to distant sites such as other organs, the brain, or bones. Pancreatic cancer is often diagnosed at this late stage because it rarely causes symptoms before it spreads to other sites. Symptoms that you may experience in this advanced stage include:
- Pain in the upper abdomen
- Back ache
- fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin)
- Anorexia
- Weight loss
- gloom
Stage IV pancreatic cancer cannot be cured, but treatments can relieve symptoms and prevent complications from the cancer. These treatments may include:
- Chemotherapy
- Palliative pain therapies
- Biliary duct bypass surgery
- bile duct stent (a stent is a small plastic or metal tube used to keep the bile duct open)
- Gastric bypass (according to statistics, the five-year survival rate for stage 4 pancreatic cancer is 3%
Stage III pancreatic cancer
Stage III pancreatic cancer is a tumor in the pancreas and possibly in nearby sites such as lymph nodes or blood vessels and has not yet spread to distant sites at this stage. This stage is called silent cancer because it is often not diagnosed until it has reached an advanced stage and stage 3 symptoms Pancreatic cancer is:
- Back ache
- Pain or tenderness in the upper abdomen
- Anorexia
- Weight loss
- fatigue
- depression
Stage 3 pancreatic cancer is difficult to treat, but treatments can help prevent the spread of cancer and relieve symptoms caused by the tumor. These treatments are:
- Surgery to remove part of the pancreas (Whipple procedure)
- Anticancer drugs
- Radiotherapy
The five-year survival rate for stage III pancreatic cancer is 3 to 12 percent.
Stage II pancreatic cancer
Stage II pancreatic cancer is cancer that remains in the pancreas and has spread to a few nearby lymph nodes. It has not spread to nearby tissues or blood vessels and has not spread to other places in the body. It is difficult to detect pancreatic cancer in the early stages, including the second stage, because it is It is unlikely to cause detectable symptoms and symptoms of this early stage are:
- jaundice
- changes in urine color
- Pain in the upper abdomen
- Weight loss
- Anorexia
- fatigue
Treatment may include:
- surgery
- radiation
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted drug therapies
Your doctor may use a combination of these techniques to help shrink the tumor and prevent possible metastasis. The “five-year” survival rate for those with stage II pancreatic cancer is about 30 percent.
Pancreatic cancer treatment
Pancreatic cancer treatment depends on the stage of the cancer and has two goals: to kill the cancer cells and prevent the spread of the disease. Weight loss, bowel obstruction, abdominal pain, and liver failure are the most common complications during treatment for pancreatic cancer.
surgery
The surgery used to treat pancreatic cancer depends on two things: the location of the cancer and the stage of the cancer.
Surgery can remove all or parts of the pancreas. This can kill the original tumor, but it will not remove cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, and surgery may not be appropriate for people with advanced pancreatic cancer for this reason.
Radiotherapy
Other treatment options should be considered once the cancer has spread beyond the pancreas. Radiation therapy uses X-rays and other high-energy beams to kill cancer cells.
Chemotherapy
In some cases, your doctor may combine chemotherapy with other treatments using cancer-killing drugs to help prevent future growth of cancer cells.
Targeted therapy
This type of cancer treatment uses drugs or other procedures to specifically target and destroy cancer cells. These drugs are designed not to harm healthy or normal cells.
Diagnosis of pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer survival rates have improved in recent decades, and new research and treatments are expanding the average “five-year survival rate” for people with pancreatic cancer.
However, the disease is still difficult to treat since pancreatic cancer usually does not cause symptoms until the cancer is in an advanced stage. Therefore, the possibility of cancer spreading is high, and this makes it difficult to treat or eliminate cancer.
But a combination of alternative measures and conventional medical treatments may help with relative improvement. Yoga, meditation and light exercise may promote relief and improvement during treatment. And early diagnosis greatly increases the chances of recovery, which is why it is best to see a doctor when you find any symptoms that do not go away or recur regularly. To make a diagnosis, the doctor reviews the symptoms and the patient’s medical history and may order one or more tests to check for pancreatic cancer, such as:
- CT or MRI scan to obtain a complete, detailed picture of the pancreas.
- Endoscopic ultrasound, where a thin, flexible tube equipped with a camera is inserted into the lower stomach to obtain images of the pancreas.
- Taking a biopsy or sample of pancreatic tissue.
- Have blood tests to check for the presence of the tumor marker CA 19-9, which could indicate pancreatic cancer.
Life expectancy for people with pancreatic cancer
Unfortunately, pancreatic cancer is one of the most deadly forms of cancer and for many patients the condition is not diagnosed until it has spread outside the pancreas. The five-year survival rate for all stages of pancreatic cancer is 9%. When all doctors’ recommendations are followed, chances of recovery and survival can be improved. You may also consider:
- Pancreatic enzyme supplements to improve digestion
- pain killers
- Regular follow-up care even if the cancer has been successfully removed.
Risk factors for pancreatic cancer
While the cause of this type of cancer is not known, there are some risk factors that may increase the chances of developing pancreatic cancer, namely:
- Cigarette smoking – 30% of cancer cases are linked to cigarette smoking
- Suffering from obesity
- Not exercising regularly
- Eat meals rich in fat
- Drinking large amounts of alcohol
- diabetes
- Work with pesticides and chemicals
- Chronic inflammation of the pancreas
- liver damage
- African Americans
A previous genetic condition of pancreatic cancer or certain genetic disorders that have been linked to this type of cancer.
Each person’s DNA has a significant impact on health and the conditions they may develop and can genetically acquire genes that increase the risk of pancreatic cancer.
Pancreatic cancer surgery
If the tumor remains confined to the pancreas, surgery may be recommended. Whether or not surgery is an option depends on the exact location of the cancer. Tumors confined to the head and neck of the pancreas can be removed with a procedure called the Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy). In this procedure, the first part, or “head,” of the pancreas, and about 20 percent of the “body,” are removed. The lower half of the bile duct and the first part of the intestine are also removed. In a modified version of this surgery, part of the stomach is also removed.
Types of pancreatic cancer
There are two types of pancreatic cancer:
Pancreatic cancer
About 95% of pancreatic cancers are adenocarcinomas. This type of cancer develops in the outermost cells, the majority of the cells in the pancreas. They are those exocrine cells that make pancreatic enzymes or form pancreatic ducts.
Pancreatic endocrine tumors ( NETs )
This less common type of pancreatic cancer develops in endocrine cells in the pancreas. These cells are responsible for producing hormones, including those that help manage blood sugar.
Prevention of pancreatic cancer
Researchers and doctors have not yet been able to know the causes of pancreatic cancer, and this also means that they do not know the steps that can be taken to prevent pancreatic cancer, but the risk factors that increase the possibility of developing this type can be reduced by making some changes in lifestyle and public health approaches, including This is amazing:
- Quit smoking: Smoking increases the risk of several types of cancer, including pancreatic cancer.
- Drinking less alcohol: reduces the risk of developing chronic pancreatitis and possibly pancreatic cancer.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese is a major risk factor for several types of cancer.
How can I book for pancreatic cancer treatment in Türkiye?

- Free medical support on the phone: You will have a dedicated representative for your health condition who is always ready to answer your questions.
- Free consultation with a specialist doctor: Your medical representative will consult with a number of doctors and hospitals to find the best possible treatments.
- Free travel visa arrangement: We will contact the embassy in your country to assist you in obtaining a visa to visit Türkiye.
- Free itinerary planning: We will create a schedule for your medical trip to Türkiye.
- Free translation of documents and reports: We will translate medical documents and reports into Turkish on your behalf.
- Free support and monitoring: We will monitor the stages of treatment and be by your side every step of the way.
- Free instant translation: We will be with you during the treatment stages to provide translation between you and the medical team.
- Free accommodation and transportation coordination: We will book accommodation for you and your companions in Türkiye, along with transportation services.
Contact REHABTÜRK doctors for more information about the procedure and to evaluate your medical condition.

